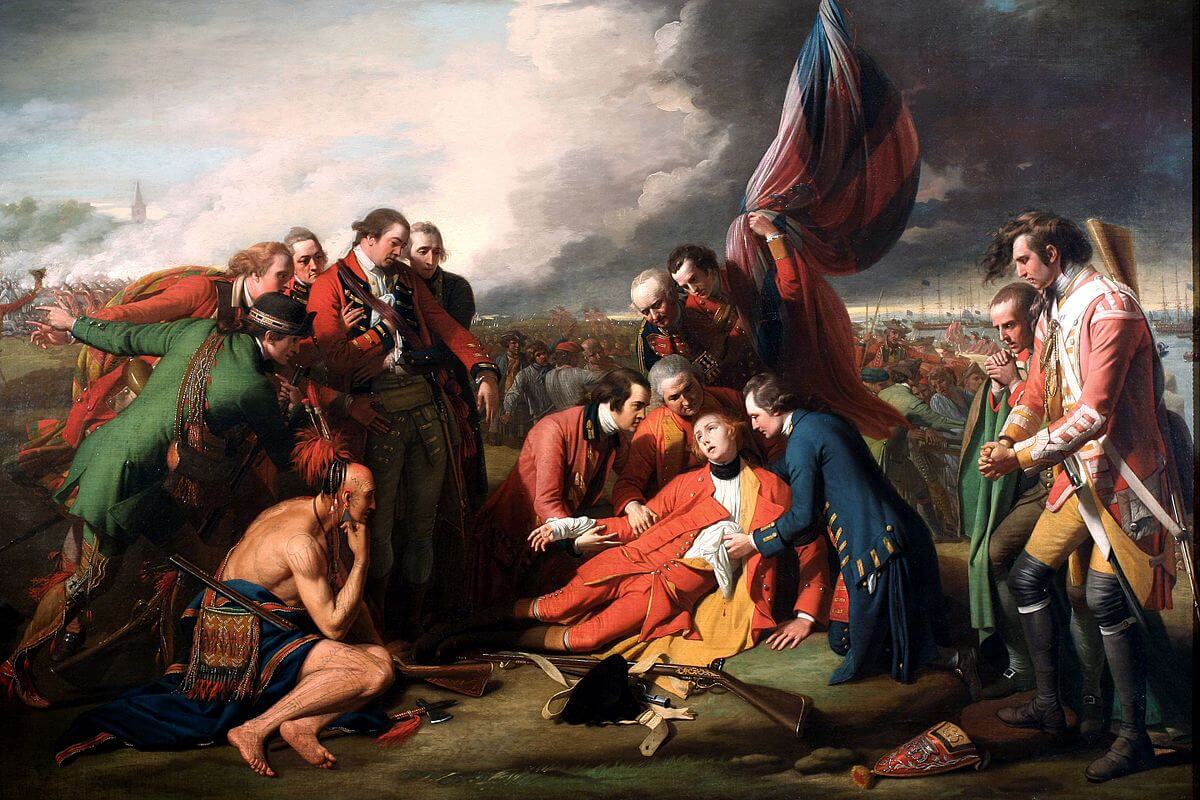
Activity 1: Can You Find It?
Find the following in the artwork:
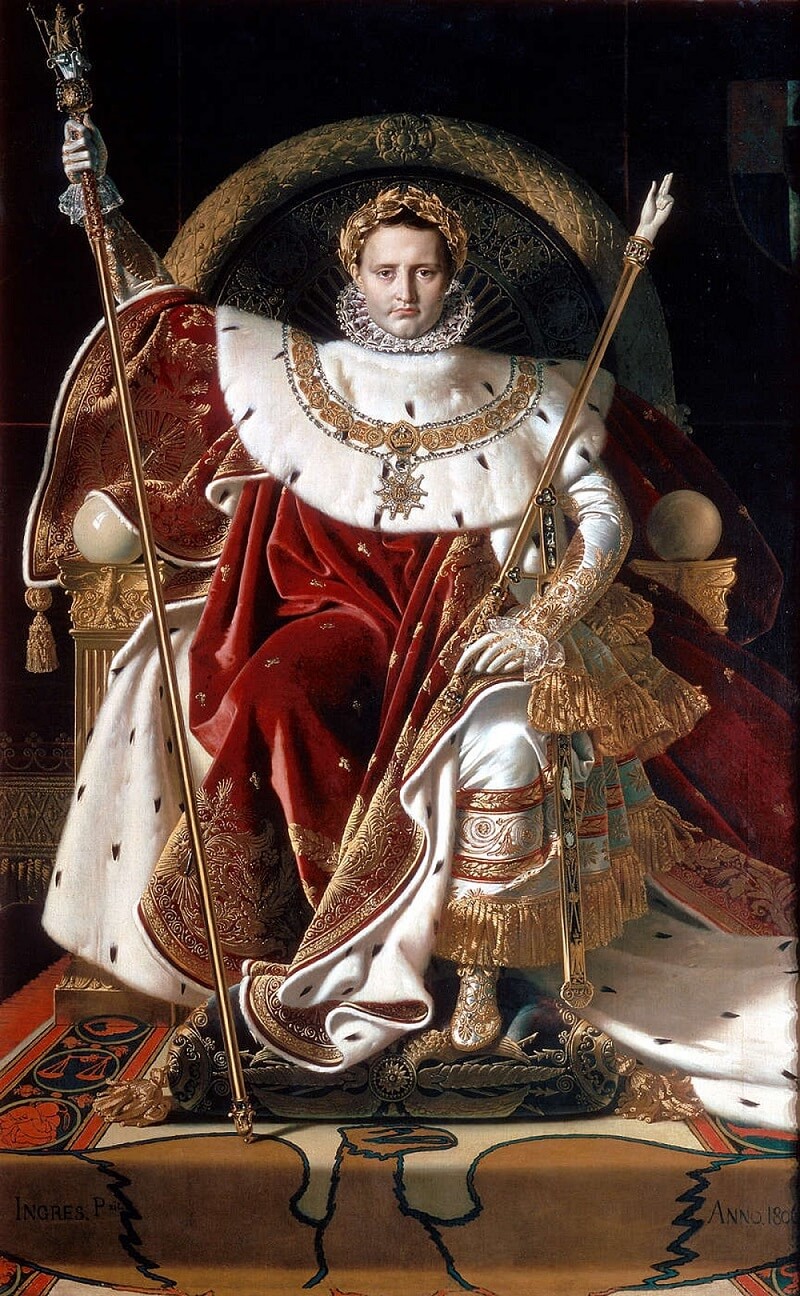
- Napoléon
- Eagles
- The Year
- Scepter
- Something Pointing
- Something Made of Ivory
- Something in a Sheathe
- The Legion of Honor
- Laurel Crown
- Throne
- Emperor
Activity 2: Narrate the Artwork
- After studying the artwork, narrate the scene shown aloud using your own words.
Activity 3: Read About the 'Napoleon Complex'
- Napoléon Bonaparte was an aggressive military leader who won many battles.
- Napoléon was ridiculed for his lack of height, although he was only an inch or so shorter than the average man at the time.
- A 'Napoleon Complex' is a derogatory phrase for domineering behavior, claimed to be a form of psychological compensation for one's short physical stature.
- See below British propaganda which mocks Napoléon for his height (Napoléon's wearing an oversized hat and sword and much shorter than the squatting British Prime Minister).
Activity 4: Classify the Artwork
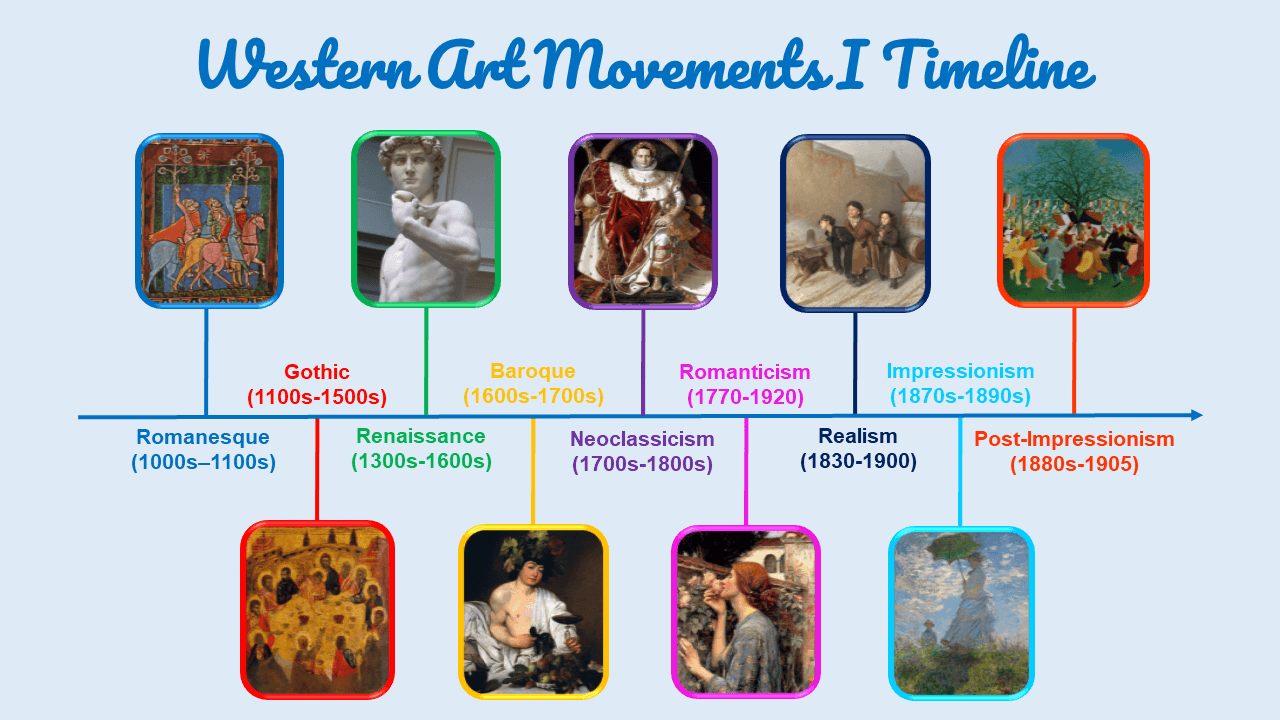
- This artwork belongs to the Neoclassical art movement.
- Find the Neoclassical art movement on the timeline.
- During which (estimated) years did the Neoclassical art movement flourish?
- Which art movement preceded the Neoclassical art movement?
- Which art movement followed the Neoclassical art movement?
Activity 5: Recreate the Artwork

- Click the crayon above and complete page 23 of 'Fourth Grade Art History Coloring Book.'
 Western Art Movements I
Art Movements
Western Art Movements I
Art Movements


 Western Art Movements I
Art Movements
Western Art Movements I
Art Movements